The success of cannabis cultivation heavily depends on lighting, as light directly influences photosynthesis, plant structure and cannabinoid production. By understanding and optimizing light spectrum and intensity, growers can enhance growth, increase yields, and improve crop quality. Leveraging modern innovations, including customizable LED systems and advanced cultivation strategies, is now a critical aspect of successful cannabis production.
The Science of Light Spectrum in Cannabis Cultivation
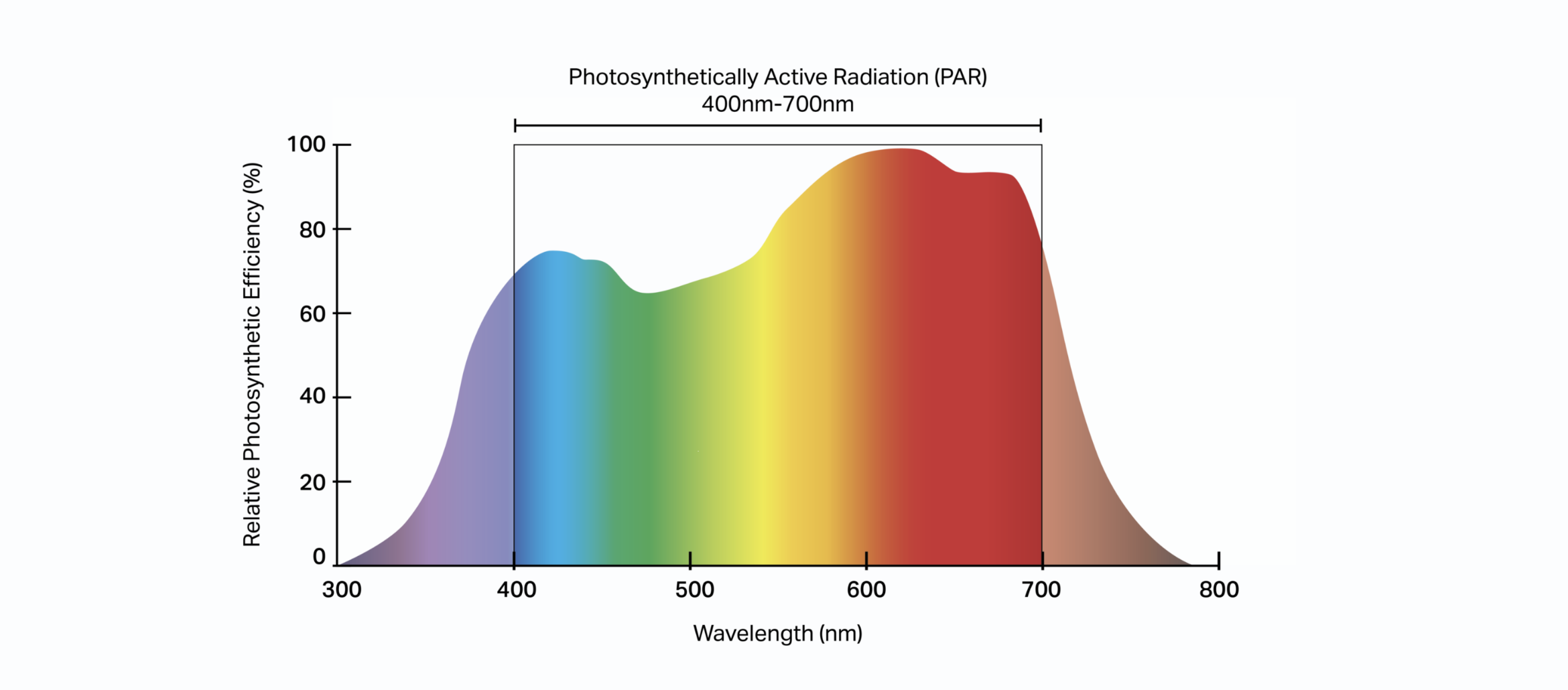
Light serves as the energy source for photosynthesis, driving plant growth from seedlings to harvest. Different wavelengths of light play unique roles in plant development:
Blue Light (400–500 nm)
- Role: Essential for vegetative growth, blue light stimulates chlorophyll production, ensuring healthy foliage and robust stems.
- Best Practices: Blue light is most effective during the seedling and vegetative stages, promoting compact, sturdy plants.
- Application: Use light sources with a color temperature of 5000K–6500K for this phase.
Red Light (620–750 nm)
- Role: Red wavelengths enhance flowering, increasing bud size and density.
- Complementary Far-Red (700–750 nm): Speeds up the flowering process by influencing photoreceptor activity, mimicking natural dusk conditions.
UV-B Light (280–315 nm)
- Role: Triggers stress responses that lead to increased trichome production, boosting cannabinoids like THC and enhancing terpene profiles.
- Caution: Overexposure can harm plants, so apply UV-B light in controlled doses during flowering stages.
Light Intensity and Its Impact
Light intensity, measured in PPFD (photosynthetic photon flux density), is as critical as spectrum optimization. Cannabis plants require varying intensity levels throughout their life cycle:
- Seedling Stage: 200–400 µmol/m²/s promotes root establishment without overstimulating young plants.
- Vegetative Stage: 400–600 µmol/m²/s supports vigorous leaf and stem growth.
- Flowering Stage: 600–1000 µmol/m²/s maximizes bud development and resin production.
Proper light intensity ensures plants receive enough energy for optimal growth while avoiding stress or bleaching.
Innovations in Lighting Technology
LED Lighting
Modern LED systems are revolutionizing cannabis cultivation with their energy efficiency, spectrum control, and low heat output.
- Customizable Spectrums: LEDs allow growers to fine-tune wavelengths for specific growth stages, from blue-heavy light for vegetative growth to red-dominant light for flowering.
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume up to 70% less energy than traditional systems, significantly reducing operational costs.
- Low Heat Output: This minimizes the need for additional cooling systems, preserving energy and protecting plants from heat stress.
Ceramic Metal Halide (CMH)
CMH lights provide a balanced spectrum similar to natural sunlight, including UV-B light.
- Benefits: Enhances terpene and cannabinoid production, making it ideal for maximizing quality.
- Drawbacks: Generates more heat than LEDs, requiring robust ventilation systems.
Advanced Plasma Lighting
Plasma lighting offers a full spectrum with high UV output, closely mimicking natural light. While effective for high-quality yields, its cost and limited availability make it less accessible for many growers.
Combining Spectrum and Intensity for Maximum Yield
Successful growers align light spectrum and intensity with the cannabis growth cycle:
- Seedling Stage
- Goal: Develop strong roots and initial foliage.
- Setup: Low-intensity blue light, such as 300 µmol/m²/s with 5000K–6500K spectrum.
- Vegetative Stage
- Goal: Promote rapid vegetative growth and robust plant structure.
- Setup: Moderate-intensity blue light, around 500 µmol/m²/s, combined with a small amount of red light to support early flowering preparations.
- Flowering Stage
- Goal: Maximize bud size, density, and resin production.
- Setup: High-intensity red-dominant light, 800–1000 µmol/m²/s, supplemented with controlled doses of UV-B light to enhance trichome development.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
Optimizing lighting not only improves crop quality but also reduces costs and environmental impact:
- Energy Savings: LEDs and efficient lighting systems significantly reduce electricity consumption.
- Sustainability: Lower heat output minimizes water evaporation, aligning with eco-friendly cultivation practices.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many jurisdictions incentivize energy-efficient systems through rebates and sustainability grants.
Future Trends in Cannabis Lighting
Emerging technologies are poised to transform cannabis cultivation further:
- AI-Driven Lighting Systems: Artificial intelligence can adjust spectrum and intensity automatically based on real-time plant needs.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Solar-powered systems and energy storage solutions are making cultivation more sustainable.
- Dynamic Spectrum Control: Innovations allow light spectrums to shift seamlessly between growth phases, reducing labor and maximizing efficiency.
Conclusion
Lighting is more than a tool for photosynthesis—it’s a critical factor in shaping the quality, potency, and yield of cannabis. By understanding the nuances of light spectrum and intensity, growers can optimize every phase of the growth cycle. Leveraging cutting-edge technologies, from customizable LEDs to advanced plasma systems, further enhances cultivation practices, ensuring competitive results in an evolving industry.